SYMBYX HEALTH PARTNERS
How does light therapy work?
How does light therapy work?
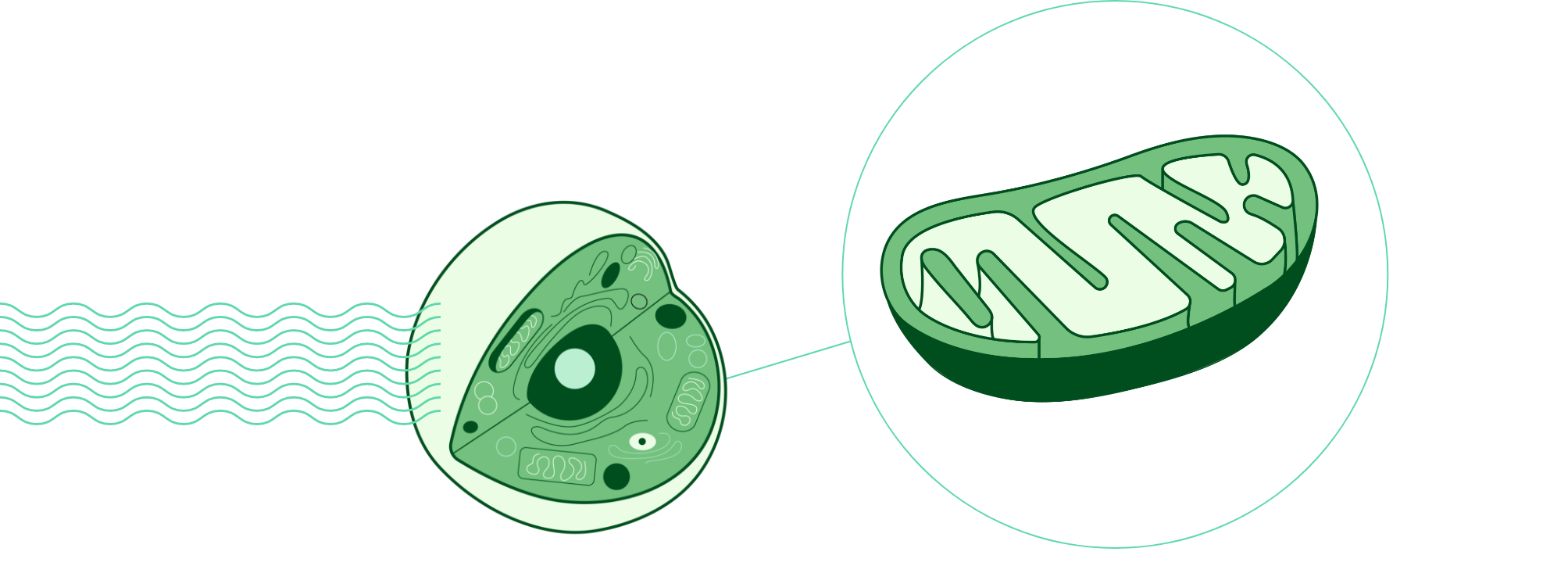

When light therapy is applied to the body, it stimulates the cellular mitochondria (the "engine house” of the cell). This leads to an increase in production of cellular energy (also known as ATP). This extra energy within the cell can then be used for growth, repair and regulating healthy cellular activities (1). Many chronic conditions such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s and chronic pain have been associated with mitochondrial insufficiency (2, 3).
Light therapy triggers the release of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species), leading to an overall anti-oxidant effect (1). Oxidative stress has been linked with many chronic conditions, including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, cancers, cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, ADHD, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD),brain fog, and more (6-9).
Red and infrared light stimulate the release of cAMP, which is a powerful anti-inflammatory (4). More specifically, cAMP helps regulate inflammation and immune cell functions. It's a known therapeutic target in both acute and chronic inflammatory conditions, as well as in autoimmune diseases (5).
Research shows that using a 904 nm infrared laser on the gut can also improve the gut microbiome (11). An unhealthy gut microbiome has been associated with many conditions, including Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, IBS, IBD, depression, anxiety, autism spectrum disorder, and more (12-16).
Light therapy releases nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation (the
widening of blood vessels) to improve blood flow (1).
Light therapy has effects on reducing pain, in both the peripheral and central nervous system. It does this by reducing inflammation and modulating nerves to create an analgesic effect (10).








Take home Range
FAQs
Laser light therapy has been studied extensively over the past 50-60 years for a range of conditions. SYMBYX lasers are ARTG and CE-listed for the reduction of pain and accelerating healing processes. Some of our devices are also listed as complementary treatments for the reduction of Parkinson's or Fibromyalgia symptoms. We also offer wellness light therapy helmets, available for home-use.
SYMBYX devices are popular with a range of clinicians, including physiotherapists, chiropractors, osteopaths, occupational therapists, acupuncturists, massage therapists, integrative GPs, specialist pain clinics, rehabilitation centres, and more. We offer both in-clinic and home-use devices.
Infrared light is generally considered anything over 800 nm, while red light is generally considered anything below that. Both have their clinical applications, depending on the intended effect. For example, red light is more effective for superficial injuries and wound healing, while infrared light is more effective for any structure requiring deeper penetration. Our ProSeries laser comes with both red and infrared light handsets.
Please contact our Customer Care team at info@symbyxbiome.com and we will reach out and answer your questions.
Class 3B and Class 4 lasers are distinguished by power levels. Both are powerful enough to be effective at a cellular level. Class 3B lasers can be safely owned and operated with as little as ensuring safety glasses are worn. Class 4 lasers pose additional risks to skin, tissue and the eyes. Hence why Class 4 lasers tend to be reserved for surgical use, where tissue destruction is intended. The majority of photobiomodulation research for treatment of neurological, metabolic, inflammatory and musculoskeletal conditions has been done using Class 3B lasers. All SYMBYX lasers are Class 3B lasers, given the specificity of the tissues and disorders that SYMBYX lasers are clinically proven to be able to treat.
A treatment session can last anywhere from 15 seconds up to 20 minutes, depending on the specific injury and type of treatment you are
administering. During your training with our clinical services team, you will learn a range of different light therapy techniques and methodologies, so you can adapt and maximise treatment for the person in front of you.
Interested? Book a call now.
References:
de Freitas LF, Hamblin MR. Proposed Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation or
Low-Level Light Therapy. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2016
May-Jun;22(3):7000417. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2016.2561201.Monzio Compagnoni G, Di Fonzo A, Corti S, Comi GP, Bresolin N, Masliah E. The Role of Mitochondria in Neurodegenerative Diseases: the Lesson from Alzheimer's Disease
and Parkinson's Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jul;57(7):2959-2980. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01926-1.Zong, Y., Li, H., Liao, P. et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction:
mechanisms and advances in therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 9, 124 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01839-8Hamblin MR. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of
photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017;4(3):337-361.Raker VK, Becker C, Steinbrink K. The cAMP Pathway as Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Immunol. 2016 Mar 31;7:123. doi:
10.3389/fimmu.2016.00123.Sharifi-Rad Mehdi, Anil Kumar Nanjangud V., Zucca Paolo, et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Frontiers in Physiology. 2020; 11. DOI=10.3389/fphys.2020.00694
Corona JC. Role of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct
23;9(11):1039. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111039.Sahoo Dipak Kumar, Heilmann Romy M., Paital Biswaranjan et al. Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2023; 14. DOI=10.3389/fendo.2023.1217165
Schiavone S, Jaquet V, Trabace L, Krause KH. Severe life stress and oxidative stress in the brain: from animal models to human pathology. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013
Apr 20;18(12):1475-90. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4720.de Sousa MVP, Kawakubo M, Ferraresi C, Kaippert B, Yoshimura EM, Hamblin MR. Pain management using photobiomodulation: Mechanisms, location, and repeatability quantified by pain threshold and neural biomarkers in mice. J Biophotonics. 2018 Jul;11(7):e201700370. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700370.
Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; McLachlan, C.S.; Kiat, H. Microbiome Changes in Humans with Parkinson’s Disease after Photobiomodulation Therapy: A Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010049
Bicknell,B.; Liebert, A.; Borody, T.; Herkes, G.; McLachlan, C.; Kiat, H.
Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Diseases and the Gut-Brain Axis: The Potential of Therapeutic Targeting of the Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119577Wang L, Alammar N, Singh R, Nanavati J, Song Y, Chaudhary R, Mullin GE. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2020 Apr;120(4):565-586. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.05.015.
Santana PT, Rosas SLB, Ribeiro BE, Marinho Y, de Souza HSP. Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol
Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3464. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073464.Clapp M, Aurora N, Herrera L, Bhatia M, Wilen E, Wakefield S. Gut microbiota's effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin Pract. 2017 Sep 15;7(4):987. doi:
10.4081/cp.2017.987.Almeida C, Oliveira R, Soares R, Barata P. Influence of gut microbiota dysbiosis on
brain function: a systematic review. Porto Biomed J. 2020 Mar 17;5(2):1-8. doi: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000059.